How the Choice Based Credit System can Improve the Quality of Higher Education in India

A robust and high-quality higher education system plays a vital role in the advancement and prosperity of any nation in today's rapidly changing world. In India, where the demand for higher education is surging, there is an urgent need to enhance the quality and relevance of educational programs. The choice-based credit system (CBCS) emerges as a revolutionary solution, offering a flexible and student-centered approach to learning.
India's statistical landscape underscores the need for reform in higher education. With over 50% of its population under the age of 25, India is home to the world's largest population of young people. However, despite this demographic advantage, the country's higher education system faces numerous challenges such as outdated curricula, rigid program structures, and inadequate emphasis on practical skills development. Consequently, a significant skills gap has emerged, with graduates lacking the necessary competencies demanded by the job market.
The Choice-Based Credit System (CBCS) is a progressive framework that empowers students to choose courses based on their interests, abilities, and career aspirations. Let’s learn how CBCS improves the quality of higher education in India in this blog post.
What is a Choice-Based Credit System (CBCS)?
The Choice-Based Credit System (CBCS) is an educational system that offers students greater freedom in choosing their courses. Each course is assigned credits based on its workload and learning outcomes. Students earn credits by successfully completing courses, which count towards their degree.
CBCS allows students to explore diverse subjects beyond the core curriculum. They can choose elective courses aligned with their interests, specialize in specific fields, or develop practical skills. This system empowers students to shape their education and pursue their academic and career aspirations.
CBCS emphasizes continuous evaluation through various assessment methods, promoting a deeper understanding of the subjects. It moves away from relying solely on final exams and encourages consistent evaluation throughout the term.
The University Grants Commission (UGC) recommends a nine-letter-grade system for CBCS evaluation, replacing percentage-based grading.
CBCS Grades and Grade Points
In the Choice Based Credit System (CBCS), the Grade “F” signifies failure, necessitating the student to retake the examination. The non-credit courses are evaluated as either 'Satisfactory' or 'Unsatisfactory' and are not factored into the computation of SGPA/CGPA. This comprehensive grading system provides a standardized evaluation method, ensuring fairness and transparency in assessing students' academic performance within the CBCS framework.
Purpose of the choice-based credit system
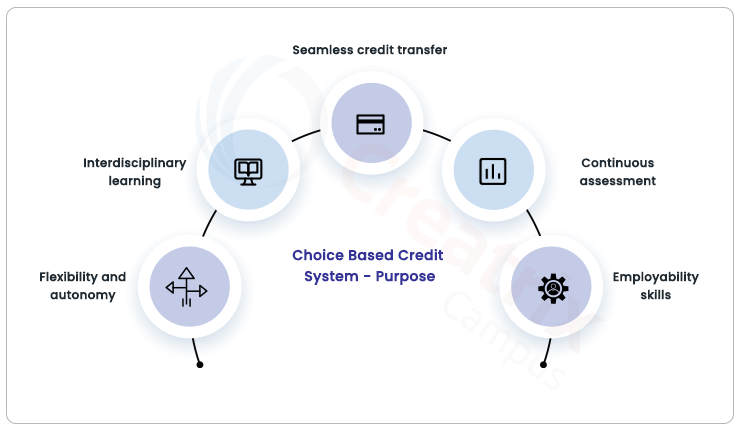
The Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) in education aims to:
Foster flexibility and autonomy: It allows students to choose courses aligned with their interests and goals, providing a wide range of electives.
Encourage interdisciplinary learning: CBCS promotes the exploration of diverse subjects, leading to a comprehensive understanding across disciplines.
Enable seamless credit transfer: The choice based credit system facilitates the transfer of earned credits between institutions, ensuring smooth educational progression.
Emphasize continuous assessment: CBCS employs various evaluation methods throughout the academic term, moving away from a sole reliance on final exams.
Enhance employability skills: It integrates skill development courses, equipping students with practical abilities for the job market.
The CBCS and quality education
The implementation of the Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) in higher education has yielded promising results for improving educational quality. Surveys and studies reveal the positive impact of CBCS on student outcomes and overall learning experiences.
According to a survey conducted by the University Grants Commission (UGC) in India, more than 70% of students reported that CBCS enhanced their learning experience through flexible course selection and interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition. Additionally, 80% of students found CBCS beneficial for develhttps://www.researchgate.net/publication/353571906_Choice_Based_Credit_System_An_Opinion_Survey_of_Students_of_Mizoram_Universityoping essential employability skills.
A study published in the Journal of Education and Practice showcased that CBCS implementation led to increased student engagement, motivation, and higher levels of critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity compared to traditional education systems.
The National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) assessed institutions following CBCS and reported improvements in overall education quality, including outcome-based learning, research orientation, and industry relevance.
These statistics and studies highlight CBCS's positive impact on enhancing educational quality by fostering student engagement, skills development, interdisciplinary learning, and aligning educational outcomes with industry needs. The CBCS framework continues to shape the future of higher education in India and beyond.
Benefits of CBCS for quality education
The Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) in higher education brings several benefits for quality education:
- Allows students to personalize their learning by selecting courses aligned with their interests and career goals.
- It promotes interdisciplinary learning, enabling students to explore diverse subjects beyond their core curriculum.
- CBCS emphasizes ongoing evaluation methods, fostering active engagement and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- It integrates skill-based courses to enhance students' employability and practical skills relevant to their chosen fields.
- CBCS facilitates seamless credit transfer between institutions, providing students with more educational mobility options.
- CBCS focuses on achieving specific learning outcomes and preparing students for real-world challenges.
Challenges in implementing CBCS for quality education
Implementing the Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) in higher education comes with certain challenges that need to be addressed for ensuring quality education:
Curriculum Design:
Developing a comprehensive and relevant curriculum that offers a wide range of courses while maintaining academic rigor can be challenging. It requires careful planning and collaboration among faculty members and subject matter experts.
Faculty Training:
Training faculty members to adapt to the CBCS framework and adopt innovative teaching methods can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. Providing professional development opportunities and support is crucial for effective implementation.
Infrastructure and Resources:
CBCS may require additional resources, such as updated infrastructure, laboratories, and technology-enabled classrooms, to accommodate the diverse course offerings and ensure a conducive learning environment.
Assessment and Evaluation:
Designing appropriate assessment methods that align with the CBCS objectives and cater to the varied learning outcomes can be complex. Continuous evaluation, timely feedback, and standardization of grading practices are vital for fair and effective assessment.
Student Guidance and Support:
With increased flexibility and course choices, students may require guidance and counseling to make informed decisions and navigate through the curriculum. Adequate student support services, academic advising, and mentoring are essential for their success.
Quality Assurance:
Ensuring quality across institutions implementing CBCS requires robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms. Regular review, accreditation processes, and adherence to prescribed standards are necessary to maintain consistent educational standards.
Best practices for successful implementation of CBCS for quality education
For successful implementation of the Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) to ensure quality education, the following best practices can be adopted:
Stakeholder engagement:
Involve all stakeholders, including faculty, students, administrators, and industry representatives, in the decision-making process and curriculum development. Collaborate with experts to align courses with industry requirements and emerging trends.
Robust infrastructure:
Establish a robust technological infrastructure to support the implementation of CBCS. This includes advanced learning management systems, online resources, and digital tools for effective course delivery, assessment, and feedback.
Faculty development programs:
Conduct regular faculty development programs to enhance teaching and assessment methods suitable for CBCS. Provide training on student-centered approaches, outcome-based education, and innovative pedagogies to ensure effective teaching and learning experiences.
Student support services:
Implement comprehensive support services, including academic counseling, mentoring, and career guidance, to assist students in course selection, credit accumulation, and career planning. Foster a supportive learning environment that caters to the diverse needs of students.
Continuous evaluation:
Emphasize continuous assessment methods such as assignments, projects, presentations, and practical examinations, along with periodic examinations. Provide timely feedback to students to facilitate their learning and improvement.
Quality assurance mechanisms:
Establish quality assurance mechanisms to monitor and evaluate the implementation of CBCS. Conduct periodic reviews, audits, and assessments to ensure compliance with prescribed standards and promote continuous improvement.
Collaboration and partnerships:
Foster collaboration with industries, research institutions, and other educational organizations to promote experiential learning opportunities, internships, and research projects. Engage in partnerships to enhance the practical applicability of CBCS and bridge the gap between academia and industry.
Conclusion
The adoption of the Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) holds immense promise for enhancing the quality of education in India. The positive impact of CBCS is evident from surveys and studies, with over 70% of students reporting enhanced learning experiences and 80% recognizing its role in developing employability skills.
Also, institutions following CBCS have showcased improvements in outcome-based learning, research orientation, and industry relevance, as reported by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC). This highlights the potential of CBCS to bridge the gap between academia and industry demands.
By implementing CBCS, institutions can foster student engagement, promote interdisciplinary learning, and align educational outcomes with industry requirements. This student-centric approach empowers learners to shape their educational journey and acquire a diverse skill set.
However, the successful implementation of CBCS requires clear communication, faculty development, collaboration, and continuous monitoring. Institutions must prioritize these best practices to ensure the effectiveness of CBCS in providing quality education.
It is crucial for educational stakeholders, including institutions, policymakers, and accrediting bodies, to recognize the transformative potential of CBCS and actively support its widespread adoption. By embracing CBCS, India can pave the way for a future-ready workforce equipped with the skills, knowledge, and adaptability needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving global landscape.
Let us collectively embrace CBCS and work towards a brighter future, where quality education prepares students to succeed in the 21st century. Contact our higher education experts to get help in implementing the CBCS in your institute.



